« Contrôle musical des bobines Tesla » : différence entre les versions
Aucun résumé des modifications |
Ajout syntherrupte |
||
| Ligne 1 : | Ligne 1 : | ||
Le Syntherrupter est un outil permettant de contrôler les bobines Telsa et de jouer des fichiers MIDI dessus. | Le Syntherrupter est un outil permettant de contrôler les bobines Telsa et de jouer des fichiers MIDI dessus. | ||
Le projet a été créé par Max Zuidberg. | Le projet a été créé par Max Zuidberg et est trouvable sur github à l'adresse suivante : https://github.com/MMMZZZZ/Syntherrupter | ||
== Enveloppes == | == Enveloppes == | ||
| Ligne 73 : | Ligne 71 : | ||
|Best approximation of an actual piano. Attack peaks to 2 (= doubling the given ontime for a few milliseconds) | |Best approximation of an actual piano. Attack peaks to 2 (= doubling the given ontime for a few milliseconds) | ||
|} | |} | ||
== Circuit imprimé == | |||
Le syntherrupter est basé sur la carte de développement TM4C1294XL de chez Ti<ref>https://www.ti.com/tool/EK-TM4C1294XL#tech-docs</ref>. Le pinout est trouvable ci-dessous. | |||
L'écran est un écran Nextion non officiel, et permet de modifier les paramètres sans reflasher la carte. | |||
[[Fichier:TM4C1294XL Pinout.png|centré|vignette|619x619px|Pinout de la carte de développement TI-TM4C1294XL<ref>https://github.com/MMMZZZZ/Syntherrupter/blob/dev/Documentation/Wiring%20and%20Schematics/TM4C1294XL%20Pinout%201.png</ref>]] | |||
Les pins utilisés par la carte de développement sur notre pcb sont les suivants : '''PD0''', '''PD2''' et '''PM0'''<ref>https://gitlab.clubelek.fr/pole-electrotech/syntherrupter</ref>. D'autres channels sont disponibles sur les pins PM2, PM4 et PM6. | |||
[[Fichier:Adaptateur usb midi.jpg|vignette|221x221px|Adaptateur USB MIDI utilisé dans le syntherrupteur]] | |||
L'écran est branché sur les pins '''PA4''' et '''PA5''' pour RX et TX. De plus, un adaptateur USB-MIDI est intégré à la carte via une daughterboard extraite d'un convertisseur USB-MIDI off-the-shelf, le modèle avec un boitier cylindrique et une vitre en plexgilas, que l'on peut trouver ici : [https://www.amazon.com/TNP-Midi-Cable-Interface-Converter/dp/B08DD6XDN1 amazon] | |||
[[Catégorie:Bobines Tesla]] | [[Catégorie:Bobines Tesla]] | ||
Dernière version du 4 janvier 2025 à 13:37
Le Syntherrupter est un outil permettant de contrôler les bobines Telsa et de jouer des fichiers MIDI dessus.
Le projet a été créé par Max Zuidberg et est trouvable sur github à l'adresse suivante : https://github.com/MMMZZZZ/Syntherrupter
Enveloppes
Principe
L'enveloppe est un moyen de modifier le son en sortie de Tesla en modulant les phases de montée et de descente d'une note.
Conversion instrument MIDI editor, enveloppe
| PRG | Linéaire | Exponentielle | Enveloppe |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Acoustic Grand Piano | No envelope. Constant ontime (except for other effects like modulation). | |
| 1 | B.A. Piano | Vibraphone | Roughly like a piano. Attack peaks to 1 (= not exceeding the given ontime) |
| 2 | E.G. Piano | Marimba | Sloooowwww rise, sloooww fall. Good for soft background, but too slow for shorter notes. Attack peaks to 1 (= not exceeding the given ontime) |
| 3 | H.T. Piano | Xylophone | Like program 1, but with a small step, to make shorter notes more audible. Attack peaks to 1 (= not exceeding the given ontime) |
| 4 | E. Piano 1 | Tubular Bells | Twice as fast as program 1. Attack peaks to 1 (= not exceeding the given ontime) |
| 5 | E. Piano 2 | Dulimer | Forced Staccato. All notes are always short. Attack peaks to 1 (= not exceeding the given ontime) |
| 6 | Harpsichord | Drawbar Organ | Forced Legato. All notes are hold for quite some time. Attack peaks to 1 (= not exceeding the given ontime) |
| 7 | Clavinette | Percussio Organ | Like program 2, but with a faster release. Attack peaks to 1 (= not exceeding the given ontime) |
| 8 | Celesta | Rock Organ | Roughly like a piano. Attack peaks to 2 (= doublingt he given ontime for a few milliseconds) |
| 9 | Glockenspeil | Church Organ | Forced Staccato with slight sustain. Attack peaks to 3 (= tripling the given ontime for a few milliseconds) |
| 10 | Music Box | Reed Organ | Best approximation of an actual piano. Attack peaks to 2 (= doubling the given ontime for a few milliseconds) |
Circuit imprimé
Le syntherrupter est basé sur la carte de développement TM4C1294XL de chez Ti[1]. Le pinout est trouvable ci-dessous.
L'écran est un écran Nextion non officiel, et permet de modifier les paramètres sans reflasher la carte.
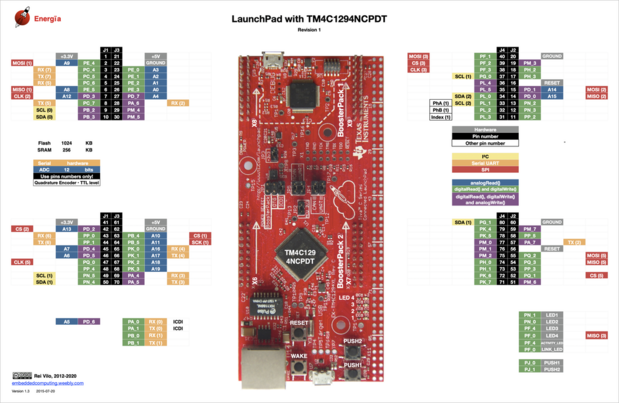
Les pins utilisés par la carte de développement sur notre pcb sont les suivants : PD0, PD2 et PM0[3]. D'autres channels sont disponibles sur les pins PM2, PM4 et PM6.

L'écran est branché sur les pins PA4 et PA5 pour RX et TX. De plus, un adaptateur USB-MIDI est intégré à la carte via une daughterboard extraite d'un convertisseur USB-MIDI off-the-shelf, le modèle avec un boitier cylindrique et une vitre en plexgilas, que l'on peut trouver ici : amazon